Radio propagation beacon
From HFUnderground
(→ITU sponsored beacons) |
(→See also) |
||
| (120 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Image:DK0WCY-station.jpg|thumb|right|DK0WCY & DRA5 beacons]] | [[Image:DK0WCY-station.jpg|thumb|right|DK0WCY & DRA5 beacons]] | ||
| - | A '''radio propagation beacon''' is a [[radio beacon]], which is used for investigating the propagation of radio signals. Currently most radio propagation beacons use [[amateur radio]] frequencies. They can be found on HF, VHF, UHF, and microwave frequencies. | + | A '''radio propagation beacon''' is a [[radio beacon]], which is mainly used for investigating the propagation of radio signals. Currently most radio propagation beacons use [[amateur radio]] frequencies.<sup>(26)</sup> They can be found on HF, VHF, UHF, and microwave frequencies. Microwave beacons are also used as signal sources to test and calibrate antennas and receivers.<sup>[1]</sup> <sup>[2]</sup> Andy Talbot, G4JNT, gives the following definition for beacons licensed in the Amateur Radio service: ''A station in the Amateur Service or Amateur Satellite Service that autonomously transmits in a fixed format, which may include repeated data or information, for the study of propagation, determination of frequency or bearing, or for other experimental purposes''.<sup>[1]</sup> |
| + | |||
| + | ==History== | ||
| + | The earliest record of radio propagation beacons goes back to World War II, when the German military operated propagation beacons on wavelengths of approximate 80 m and 10 m. Many propagation beacons were installed during the International Geophysical Year 1957-1958 These included amateur radio beacons OZ7IGY and GB3IGY (later GB3RAL) on 144 MHz, which are still operational, as well as the now defunct DM3IGY in East Germany on 28001 kHz. <sup>(19)</sup> GB3IGY transmitted with the unusual for the time high power of 1 kW. It was situated at Badgers Mount, Sevenoaks, England and was operated by Ken Ellis, G5KW.<sup>(22)</sup> | ||
==Transmission characteristics== | ==Transmission characteristics== | ||
| + | [[File:WB0RIO-CW-beacon.jpg|thumb|right|A CW beacon keyer based on discrete CMOS digital chips.]] | ||
| + | The majority of propagation beacons operate in continuous wave (CW or A1A) and transmit their identification (callsign and location) in Morse code. Some of them send long dashes (sometimes at varying power levels) to facilitate signal strength measurement. A small number of beacons transmit Morse code by frequency shift keying (F1A). A few beacons transmit signals in digital modulation modes, like [[RTTY|radioteletype]] (F1B) and [[PSK31]] (G1B). | ||
| - | Most beacons | + | Most beacons consist of a simple digital keyer, based on discrete digital electronics or a microcontroller, and a low power transmitter or tranceiver. FT-897, a budget HF tranceiver produced by Yaesu/Vertex, has a programmable beacon mode and is used in some temporary propagation beacon installations. Recently K6HX published a versatile Morse code keyer design based on the popular Arduino microcontroller platform. |
| - | + | Antennas usually are types with low directivity. There are exceptions, however, like the high power beacons with directional antennas, specifially set up for transatlantic VHF propagation experiments. | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
==160 meters beacons== | ==160 meters beacons== | ||
| Line 16: | Line 19: | ||
==60 meters beacons== | ==60 meters beacons== | ||
| - | In addition to the DARC and RSBG beacon projects on 5195 and 5290 kHz (see below), Eddie Bellerby of [[UDXF]] discovered in March 2011 a new CW beacon on 5206 kHz, sending LX0HF, presumably from Luxembourg.<sup>[13]</sup> Further intelligence indicates that the beacon is operated by Philippe LX2A/LX7I of the Luxembourg Amateur Radio Society.<sup>[14]</sup> Two more european beacons are listed on 5 MHz, OV1BCN on 5290 kHz, operated by OZ1FJB and OK1IF on 5258.5 kHz from the Czech Republic, though their current status is unclear. | + | In addition to the DARC and RSBG beacon projects on [[Fixed/Mobile_bands|5195 and 5290 kHz]] (see below), Eddie Bellerby of [[UDXF]] discovered in March 2011 a new CW beacon on 5206 kHz, sending LX0HF, presumably from Luxembourg.<sup>[13]</sup> Further intelligence indicates that the beacon is operated by Philippe LX2A/LX7I of the Luxembourg Amateur Radio Society.<sup>[14]</sup> Two more european beacons are listed on 5 MHz, OV1BCN on 5290 kHz, operated by OZ1FJB and OK1IF on 5258.5 kHz from the Czech Republic, though their current status is unclear. |
{| border="1" cellspacing="0" cellpadding="5" align="center" | {| border="1" cellspacing="0" cellpadding="5" align="center" | ||
| Line 24: | Line 27: | ||
| DRA5 || 5195.0 kHz || JO44VQ || DARC | | DRA5 || 5195.0 kHz || JO44VQ || DARC | ||
|- | |- | ||
| - | | LX0HF || 5205.3 kHz || | + | | LX0HF || 5205.2 kHz || JN39dr || Radioamateurs du Luxembourg [http://www.rlx.lu/de/qso/repeaters/beacons.html] |
| + | |- | ||
| + | | HG7BHB || 5252.3 kHz || JN97LE || | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | OK1IF || 5258.5 kHz || JO40HG || Inactive. Recording: [http://ok1if.c-a-v.com/5MHzOK/OK4AS.WAV] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | GB3RAL || 5290.0 kHz || IO91IN || RSGB, inactive | ||
|- | |- | ||
| - | | | + | | GB3WES || 5290.0 kHz || IO84QN || RSGB, inactive |
|- | |- | ||
| - | | | + | | GB3ORK || 5290.0 kHz || IO89JA || RSGB, inactive |
|- | |- | ||
| - | | | + | | OV1BCN || 5290.5 kHz || JO55SI || Op OZ1FJB [http://www.oz1fjb.dk/page8.html] |
|- | |- | ||
| - | | | + | | HB9AW || 5291.0 kHz || JN47BE || [https://www.hb9aw.ch/bake-5000khz/] |
|- | |- | ||
| - | | | + | | SZ1SV || 5398.5 kHz || KM17UX || Op SV1IW & SV1JG. Inactive. |
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 79: | Line 88: | ||
==40 MHz beacons== | ==40 MHz beacons== | ||
| - | * The first radio propagation beacon on 40 MHz is OZ7IGY in Jystrup, Denmark (JO55WM) and transmits on 40021 kHz. Transmitted power is | + | * The first radio propagation beacon on 40 MHz is OZ7IGY in Jystrup, Denmark (JO55WM) and transmits on 40071 kHz <s>40021 kHz</s> (40.071 MHz). Transmitted power is 20 W to a dipole antenna. <!-- Modulation is F1A keying (frequency Shift Keying), with a shift of 250 Hz. [http://www.oz7igy.dk/] --> The beacon is frequency- and time-locked to GPS. The sequence is programmed to send PI4 , followed by a short pause, and then the call sign and grid locator sent in CW, then a pause, and a carrier until start of the next cycle. PI4 is a digital mode specifically designed for beacons and propagation studies, similar to JT4 and WSPR. To decode PI4, tune 800 Hz below the nominal frequency. |
| - | * The [[Radio Society of Great Britain]] has a license for beacon transmissions from GB3RAL (Didcot, UK) on 40050 & 60050 kHz. | + | * The [[Radio Society of Great Britain]] has a license for beacon transmissions from GB3RAL (Didcot, UK) on 40050 & 60050 kHz (40.050 MHz & 60.050 MHz - 8 meters and 5 meters). |
| + | * While not a beacon by design, the US Government's SNOTEL telemetry system [[SINCGARS#Federal_Government_and_Military_Only_Bands_30-50_MHz|on 40 MHz]] operates more than 600 transmitters (mostly in the Rocky Mountain and Western United States regions) on 40670 kHz (40.670 MHz, 40.67 MHz). During sporadic-E band openings, data bursts from the SNOTEL system can be heard on 40.67 MHz. | ||
| + | * The Canadian [[SINCGARS#Confirmed_30-88_MHz_and_30-50_MHz_FM_Military_Frequencies_In_Use_North_America_USA|military]] base Shuffield (CYSD) in Alberta operates a FM mode [[SINCGARS|military]] VHF FM radio beacon transmitting continuously with a CW ID / a Morse code ID '''YSD''' followed by a tone burst on 36.6 FM (36600 kHz FM, 36.600 MHz FM, 36.60 FM, 36.6 MHz). | ||
==6 meters (50 MHz) beacons== | ==6 meters (50 MHz) beacons== | ||
[[Image:LX0FOUR antenna.jpg|thumb|right|Antenna tower of LX0SIX and LX0FOUR beacons]] | [[Image:LX0FOUR antenna.jpg|thumb|right|Antenna tower of LX0SIX and LX0FOUR beacons]] | ||
| - | In the 6 meters (50 MHz) band, beacons operate in the lower part of the band, in the range 50000 kHz to 50080 kHz | + | In the 6 meters (50 MHz) band, beacons traditionally operate in the lower part of the band, in the range 50000 kHz to 50080 kHz. Due to unpredictable and intermittent long distance propagation, usually achieved by a combination of ionospheric conditions, beacons are very important in providing early warning for 50 MHz openings. |
| + | |||
| + | The ARRL bandplan recommends 50060 to 50080 kHz for beacons in the United States. | ||
| + | |||
| + | In Australia beacons operate from 50280 to 50350 kHz. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The new IARU Region 1 bandplan moves 50 MHz beacons, with the exception of beacons participating to the Synchronized Beacon Project, in a new allocation, 50400 to 50500 kHz. | ||
==4 meters (70 MHz) beacons== | ==4 meters (70 MHz) beacons== | ||
| Line 96: | Line 113: | ||
===Special beacon allocations=== | ===Special beacon allocations=== | ||
| - | * USA: 70.005 MHz is allocated to the WE9XFT beacon. Transmits from Bedford, VA, under an FCC experimental license issued to Brian Justin, WA1ZMS, with a power of 3 kW. | + | * USA: 70.005 MHz is allocated to the WE9XFT beacon. Transmits from Bedford, VA, under an FCC experimental license issued to Brian Justin, WA1ZMS, with a power of 3 kW. In 2012 this beacon shall transmit from the same location under new callsign WF9XRU. |
* Austria: 70.045 MHz is allocated to the OE5QL beacon. | * Austria: 70.045 MHz is allocated to the OE5QL beacon. | ||
* Hong Kong: 71.757 MHz is allocated to the VR2FOUR beacon. | * Hong Kong: 71.757 MHz is allocated to the VR2FOUR beacon. | ||
| Line 111: | Line 128: | ||
! colspan="3" | Beacon Sub-band (MHz) | ! colspan="3" | Beacon Sub-band (MHz) | ||
|- style="background: #E7E7FF" | |- style="background: #E7E7FF" | ||
| - | ! R1 | + | ! align="center" |IARU R1 |
| - | ! R2 | + | ! align="center" | IARU R2 |
| - | ! R3 | + | ! align="center" |IARU R3 |
|- | |- | ||
| align="center" | 2 m | | align="center" | 2 m | ||
| Line 167: | Line 184: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===ON0EME moon beacon=== | ||
| + | [[File:ON0EME capture.jpg|thumb|right|Screen capture of ON0EME by G4DZU]] | ||
| + | A beacon specifically for earth-moon-earth (EME or "moonbounce") reception became operational in 2012 in Belgium. The beacon uses call sign ON0EME and transmits on 1296.0 MHz with a very high power of 1000 kW ERP. The antenna is a solid parabolic reflector with a diameter of 3.7 m. <sup>[17]</sup> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===144 MHz transatlantic beacons=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | A number of VHF beacons have been installed on both shores of the Atlantic Ocean, as an early warning system for exceptional sporadic-E (Es) conditions, which shall allow transatlantic QSOs on 2 m. The followng list includes most beacons, not all of them are always operational.<sup>[23]</sup> | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| border="1" cellspacing="0" cellpadding="5" align="center" | ||
| + | |- style="background: #E7E7FF" | ||
| + | ! Callsign !! Locator !! Frequency (kHz) !! Info | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | CU2VHF || HM77DT || 144401 || | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | CU8DUB || HM49KL || 144420 || | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | D4C/B || HK76MV || 144436 || 750 m ASL, 20W CW. Copied by Dave Pedersen, PJ4VHF/N7BHC, on Bonaire Island on May 6, 2015 [http://www.arrl.org/news/cape-verde-2-meter-beacon-heard-in-bonaire] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | ED8ZAA/B || IL18 || 144484 || | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | GB3WGI<sup>[24]</sup> || IO64BL || 144487 || 100 W CW and JT65. Activated on June 4, 2013. | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | K4MHZ || FM25 || 144300 || 2M Transatlantic Beacon, Hatteras, NC: CW at 10 WPM. Running 100W to a 12 element long Yagi at 50' on a center azimuth of 70 degrees towards the Azores, Canary Islands, and southern Europe/North Africa. | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | N7BHC || FM15PA || 144291 || Mode: CW, 13 WPM. Transmit sequence: N7BHC FM15PA N7BHC FM15PA N7BHC FM15PA (15 second carrier) (15 seconds receive period). Location: 35.0302 N - 76.7146 W | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | NP2X/B || FK77PR || 144291 || St. Croix, US Virgin Islands - 240 feet AMSL (73 meters AMSL) - RF Concepts 160 watt, reduced to 100 watts for beacon operation - 15 element yagi @ beam heading of 55 degrees (Portgual) - np2xbeacon@gmail.com | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | PY2MTV/B || GG66va || 144300 || Beaming to AF/EU | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | VE1SMU/H || || 144.288 || | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | VO1ZA || GN37JS || 144400 || Inactive | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | W1RJA/B || FN41CJ || 144282 || Southern Rhode Island. Emission: A1 (amplitude keyed CW) Power: 60 Watts Feedline: 160' Cablewave FLC 12-50 half inch hardline. Antenna: 9.5 dBd 5 element yagi beaming 60 degrees azimuth. Height: 140 feet (43M) above base elevation of 130 feet (40M) ASL | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | WA1ZMS || FM07FM || 144285 || Activated on October 29, 2006 - 4200FT AMSL - Antenna: 2-yagi pair, Directive Systems DPM144-5 Antenna gain: 11.5dBd Radiated power: 1400W ERPd) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Indian Ocean beacon project=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | An Australian ham radio group has set up a beacon to investigate if there is any VHF ducting between Australia and South Africa. Beacon VK6RIO is located in Perth, W. Australia and operates on 144.950 MHz. The beacon transmits 100 watts into four 8-element Yagis with digital Chirp modulation. This special modulation scheme can be detected some 50 dB below the noise floor. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The beacon is GPS locked both in frequency, time and Chirp synchronisation. In order to detect the Chirp beacon, the receiving station requires a GPS locked [[Software Defined Radio]] (SDR), a GPS locked 144 MHz down-converter and 1 PPS signal from a GPS receiver to time stamp received signals. Open source PC software by Hermann, DL3HVH, shall be made available for processing the received signals. | ||
==SHF and microwave beacons== | ==SHF and microwave beacons== | ||
| Line 177: | Line 240: | ||
! colspan="3" | Beacon Sub-band (MHz) | ! colspan="3" | Beacon Sub-band (MHz) | ||
|- style="background: #E7E7FF" | |- style="background: #E7E7FF" | ||
| - | ! R1 | + | ! align="center" |IARU R1 |
| - | ! R2 | + | ! align="center" |IARU R2 |
| - | ! R3 | + | ! align="center" |IARU R3 |
|- | |- | ||
| align="center" | 9 cm | | align="center" | 9 cm | ||
| Line 194: | Line 257: | ||
| align="center" | 10,368.800-10,368.995 | | align="center" | 10,368.800-10,368.995 | ||
| align="center" | 10,368.300-10,368.400 | | align="center" | 10,368.300-10,368.400 | ||
| - | | align="center" | Unknown | + | | align="center" | Unknown <sup>(25)</sup> |
|- | |- | ||
| align="center" | 1.2 cm | | align="center" | 1.2 cm | ||
| - | | align="center" colspan=" | + | | align="center" | 24,048.800-24,048.995 |
| + | | align="center" colspan="2"| Beacons are rare | ||
|} | |} | ||
| - | == | + | ==Optical and infrared beacons== |
| + | Recently some groups of [[amateur radio|radio amateurs]], especially in Great Britain, experiment with two-way communications on optical wavelengths. This activity has led to the design and installation of a few beacons operating on optical wavelengths. These beacons transmit modulated light using high intensity LEDs and are used mainly for equipment setting and calibration. An interesting example is the optical beacon located at GB3CAM (Wyton, UK) operating at 628 nm.<sup>[16]</sup> | ||
| + | ==License-free experimental beacons== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Main articles: ''[[LowFER]]'', ''[[HiFER]]''. | ||
| + | |||
| + | These are extremely low power experimental beacons which operate legally without a license on specific bands, which are reserved for very short range radio transmissions or for industrial, scientific and medical devices (ISM) and in which a limited level of radiated RF energy is allowed. They are operated as radio propagation experiments by radio amateurs and other radio hobbyists. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | {| border="1" cellspacing="0" cellpadding="5" align="center" | ||
| + | |- style="background: #E7E7FF" | ||
| + | ! Type !! Frequencies !! Countries !! [[FCC]] Part 15 rules | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | [[LowFER]] || 160-190 kHz || USA, Canada || § 15.217 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | MedFER || 510 & 1704 kHz<BR>(510-1705 kHz) || USA, Canada || § 15.219 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | BeFER || 6776 kHz || Canada || - | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | [[HiFER]] || 13553-13567 kHz || USA, Canada || § 15.225 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 49ers || 49846 kHz<BR>(49820-49900 kHz) || USA || § 15.235 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Beacon projects== | ||
| + | [[File:TS-50S NCDXF beacon.png|thumb|right|NCDXF-IARU beacon setup]] | ||
Most radio propagation beacons are operated by individual radio amateurs or amateur radio societies and clubs. As a result, there are frequent additions and deletions to the lists of beacons. There are, however a few major projects coordinated by organizations like the [[International Telecommunications Union]] and the International Amateur Radio Union. | Most radio propagation beacons are operated by individual radio amateurs or amateur radio societies and clubs. As a result, there are frequent additions and deletions to the lists of beacons. There are, however a few major projects coordinated by organizations like the [[International Telecommunications Union]] and the International Amateur Radio Union. | ||
| - | ===IARU Beacon Project=== | + | ===IARU/NCDXF HF Beacon Project=== |
[[Image:IARU.gif|left|50px|url="http://www.darc.de"]] | [[Image:IARU.gif|left|50px|url="http://www.darc.de"]] | ||
The International Beacon Project (IBP), which is coordinated by the Northern California DX Foundation (NCDXF) and the International Amateur Radio Union (IARU), consists of 18 HF propagation beacons worldwide, which transmit in turns on 14100 kHz, 18110 kHz, 21150 kHz, 24930 kHz, and 28200 kHz. <sup>[5]</sup> The IARU/NDXF beacons transmit in turns on the five designated frequencies according to the following schedule, which repeats every 3 minutes: | The International Beacon Project (IBP), which is coordinated by the Northern California DX Foundation (NCDXF) and the International Amateur Radio Union (IARU), consists of 18 HF propagation beacons worldwide, which transmit in turns on 14100 kHz, 18110 kHz, 21150 kHz, 24930 kHz, and 28200 kHz. <sup>[5]</sup> The IARU/NDXF beacons transmit in turns on the five designated frequencies according to the following schedule, which repeats every 3 minutes: | ||
| Line 250: | Line 340: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| - | The original NCDXF/IARU beacon project, coordinated by John W6ISQ, consisted of nine 100W beacons which operated only on 14100 kHz on a coordinated 10 minute sequence. The beacons used to send a longer callup sequence, like "QST DE 4U1UN/B BEACON" followed by dashes with 100 W, 10 W, 1 W, and 100 mW, finally ending with "4U1UN/B SK". The original beacons were 4U1UN/B, W6WX/B, KH6O/B, JA2IGY, 4X6TU, OH2B, CT3B, ZS6DN and LU4AA. This network evolved into its current format with 18 beacons on five frequencies around 1999.<sup>(15)</sup> | + | The original NCDXF/IARU beacon project, coordinated by John W6ISQ, consisted of nine 100W beacons which operated only on 14100 kHz on a coordinated 10 minute sequence. The beacons used to send a longer callup sequence, like "QST DE 4U1UN/B BEACON" followed by dashes with 100 W, 10 W, 1 W, and 100 mW, finally ending with "4U1UN/B SK". The original beacons were 4U1UN/B, W6WX/B, KH6O/B, JA2IGY, 4X6TU, OH2B, CT3B, ZS6DN and LU4AA. This network evolved into its current format with 18 beacons on five frequencies around 1999.<sup>(15)</sup> The current beacons consist of a Kenwood TS-50 tranceiver, a beacon controller, a vertical antenna and a GPS unit. |
| - | + | ||
{{Clear}} | {{Clear}} | ||
===ITU sponsored beacons=== | ===ITU sponsored beacons=== | ||
| - | As part of an International Telecommunications Union-funded project, radio propagation beacons were installed by national authorities at Sveio, Norway (callsign LN2A, 59.6042<sup>0</sup>N - 5.29167<sup>0</sup>E) and at Darwin, Australia (callsign VL8IPS, 12.6042<sup>0</sup>S - 131.2920<sup>0</sup>E). The beacons operated on frequencies 5471.5 kHz, 7871.5 kHz, 10408.5 kHz, 14396.5 kHz, and 20948.5 kHz.<sup>(6)</sup> <sup>(15)</sup> Since 2002, there have been no reception reports for these beacons and the relevant ITU web pages have been removed. <sup>(7)</sup> | + | As part of an International Telecommunications Union-funded project, radio propagation beacons were installed by national authorities at Sveio, Norway (callsign LN2A, 59.6042<sup>0</sup>N - 5.29167<sup>0</sup>E) and at Darwin, Australia (callsign VL8IPS, 12.6042<sup>0</sup>S - 131.2920<sup>0</sup>E). The beacons operated on frequencies 5471.5 kHz, 7871.5 kHz, 10408.5 kHz, 14396.5 kHz, and 20948.5 kHz.<sup>(6)</sup> <sup>(15)</sup> <sup>(27)</sup> Since 2002, there have been no reception reports for these beacons and the relevant ITU web pages have been removed. <sup>(7)</sup> <sup>(20)</sup> |
| - | {| border="1" cellspacing="0" cellpadding="5" align="center" | + | |
| - | + | {| border="1" cellspacing="0" cellpadding="5" align="center" style="background: #F3F3FF" | |
| + | |- | ||
| '''HF Field-Strength measurement campaign''' | | '''HF Field-Strength measurement campaign''' | ||
| Line 265: | Line 355: | ||
The reasons for the campaign and the continuing need for participation in it, are underlined in Resolution ITU-R 27 (HF field-strength measurement campaign). So far, regular transmissions are being provided by the Administrations of Australia and Norway. Details of the transmitter in Norway, operated by the Norwegian Telecommunications Authority and Telenor Broadcasting, are given below: | The reasons for the campaign and the continuing need for participation in it, are underlined in Resolution ITU-R 27 (HF field-strength measurement campaign). So far, regular transmissions are being provided by the Administrations of Australia and Norway. Details of the transmitter in Norway, operated by the Norwegian Telecommunications Authority and Telenor Broadcasting, are given below: | ||
| - | '''Radio Beacon LN2A''' | + | |- |
| + | | '''Radio Beacon LN2A''' | ||
| + | [[File:QSL LN2A front.jpg|right|200px]] | ||
| + | [[File:QSL LN2A back.jpg|right|200px]] | ||
* Identification signal (Morse code): LN2A | * Identification signal (Morse code): LN2A | ||
* Location: Sveio, Norway 59 deg 37 min N, 5 deg 19 min E | * Location: Sveio, Norway 59 deg 37 min N, 5 deg 19 min E | ||
| Line 278: | Line 371: | ||
* Signal duration and format: as specified in Recommendation ITU-R P.845; 4 min for each frequency, 20 min for all five frequencies according to the following schedule: | * Signal duration and format: as specified in Recommendation ITU-R P.845; 4 min for each frequency, 20 min for all five frequencies according to the following schedule: | ||
| - | {| | + | {| style="background: #F3FFF3" |
! Reference frequency (kHz) !! Minutes after each hour | ! Reference frequency (kHz) !! Minutes after each hour | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 302: | Line 395: | ||
N-0104 Oslo <BR> | N-0104 Oslo <BR> | ||
Norway <BR> | Norway <BR> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | '''Radio Beacon VL8IPS''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | This beacon was established by IPS Radio and Space Services in conjuction with thw Royal Australian Navy. | ||
| + | * Identification signal (in Morse code): VL8IPS | ||
| + | * Location: Humpty Doo, near Darwin, Northen Territory, 12 deg 36 min S - 131 deg 16 min 51 sec E | ||
| + | * Hours of transmission: 24 hours per day | ||
| + | * Assigned frequencies: 5470 kHz, 7870 kHz, 10407 kHz, 14395 kHz and 20945 kHz | ||
| + | * Transmitter: Rockwell Collins HF-8022 | ||
| + | * Transmitter power: approximately 2 kW on all frequencies | ||
| + | * Antenna: AEA 628D biconical monopole | ||
| + | * Mode: suppressed carrier SSB (USB & LSB) with the reference frequencies (suppressed carrier frequencies) 1225 Hz below the assigned frequencies, with the FSK "mark" 800 Hz above reference frequency and the FSK "space" 1650 Hz above the reference frequency. | ||
| + | * Signal duration and format: as specified in Recommendation ITU-R P.845; 4 min for each frequency, 20 min for all five frequencies according to the following schedule: | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| style="background: #F3FFF3" | ||
| + | ! Reference frequency (kHz) !! Minutes after each hour | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | align="center" | 5470 || align="center" | 00 - 20 - 40 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | align="center" | 7870 || align="center" | 04 - 24 - 44 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | align="center" | 10407 || align="center" | 08 - 28 - 48 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | align="center" | 14395 || align="center" | 12 - 32 - 52 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | align="center" | 20945 || align="center" | 16 - 36 - 56 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Reception reports could be sent beacon@ips.gov.au | ||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 316: | Line 440: | ||
The [[Radio Society of Great Britain]] (RSGB) operates three radio propagation beacons on 5290 kHz, which transmit in sequence, for one minute each, every 15 minutes. The project includes GB3RAL near Didcot (51.5625<sup>0</sup>N - 1.29167<sup>0</sup>W, IO91IN), GB3WES in Cumbria (54.5625<sup>0</sup>N - 2.625<sup>0</sup>W, IO84QN) and GB3ORK in the Orkney Islands (59.0208<sup>0</sup>N - 3.20833<sup>0</sup>W, IO89JA). | The [[Radio Society of Great Britain]] (RSGB) operates three radio propagation beacons on 5290 kHz, which transmit in sequence, for one minute each, every 15 minutes. The project includes GB3RAL near Didcot (51.5625<sup>0</sup>N - 1.29167<sup>0</sup>W, IO91IN), GB3WES in Cumbria (54.5625<sup>0</sup>N - 2.625<sup>0</sup>W, IO84QN) and GB3ORK in the Orkney Islands (59.0208<sup>0</sup>N - 3.20833<sup>0</sup>W, IO89JA). | ||
| - | Beacon GB3RAL, which is located at the Rutherford-Appleton Laboratory, also transmits continuously on 28215 kHz and on a number of low VHF frequencies (40050, 50053, 60053 and 70053 kHz).<sup>[10]</sup> | + | Beacon GB3RAL, which is located at the Rutherford-Appleton Laboratory (RAL), also transmits continuously on 28215 kHz and on a number of low VHF frequencies (40050, 50053, 60053 and 70053 kHz).<sup>[10]</sup> |
| - | === U.S. Navy | + | As of August 2017 the 5 MHz beacon at Didcot is not operational. The other two beacons are active. In addition to Morse code, beacon GB3ORK also transmits in JT9 on the minute following its regular transmission. |
| - | A radio propagation beacon with callsign NAF was installed in 1983 | + | |
| + | === U.S. Navy beacons === | ||
| + | A radio propagation beacon with callsign NAF was installed in 1983 at Cape Prince, Wales, AK. It transmitted both CW and FSK identification with 100 W to a three-band fan dipole on 5604, 11004 and 16804 kHz. The project, which included reception sites at Fairbanks, AK, Seattle, WA, State College, PA and San Diego, CA, was coordinated by the U.S. Naval Security Group Command and its purpose was to verify and calibrate HF propagation prediction software. <sup>(15)</sup> It is not known when the project was terminated. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Another propagation beacon was installed in 1991 at the Arctic Submarine Laboratory at Cape Prince of Wales, AK. The beacon operated on [[11_meter|25545 kHz (25.545 MHz)]] and tranmitted the morse code letter "R". A reception facility existed at Fairbanks, AK, some 900 km away. The R beacon was used to study aurora and sporadic E events at high geographical latitudes.<sup>(18)</sup> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===WSPR Network=== | ||
| + | This is an a large scale [[amateur radio]] propagation beacon project which uses the WSPR (Weak Signal Propagation Reporter) transmission scheme available with the WSJT software suite, created by Joe Taylor, K1JT. The loosely-coordinated beacon transmitters and receivers, collectively known as the WSPRnet, report the real-time propagation characteristics of a number of frequency bands and geographical locations via the Internet. The [http://wsprnet.org/drupal/ WSPRnet website] provides detailed propagation report databases and real-time graphical maps of propagation paths. WSPR Network operates on the following amateur radio frequencies (USB dial settings in kHz) 136.0, 502.4, 1836.6, 3592.6, 5287.2, 7038.6, 101387.0, 14095.6, 18104.6, 21094.6, 24924.6, 28124.6, 50293.0, 70028.6 and 144489.0 kHz. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===IARU 50 MHz Synchronized Beacon Project (SBP)=== | ||
| + | IARU promotes a network of synchronized beacons worldwide at the lower part of the 50 MHz (6m) band. Each IARU region is allocated a 10 kHz segment, which is divided into ten 1 kHz wide beacon channels. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| border="1" cellspacing="0" cellpadding="5" align="center" | ||
| + | |- style="background: #E7E7FF" | ||
| + | ! IARU Region | ||
| + | ! Beacon frequencies (kHz) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | align="center" | '''R1''' | ||
| + | | 50000, 50001, 50002, 50003, 50004, 50005, 50006, 50007, 50008, 50009 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | align="center" | '''R2''' | ||
| + | | 50010, 50011, 50012, 50013, 50014, 50015, 50016, 50017, 50018, 50019 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | align="center" | '''R3''' | ||
| + | | 50020, 50021, 50022, 50023, 50024, 50025, 50026, 50027, 50028, 50029 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | Each frequency can accomodate up to five beacons, which transmit sequentially in time slots (TS) 0 to 4. The transmission mode and sequence for each beacon is "PI4 - CW ID - carrier", lasting exactly one minute. SBP beacons transmit with 25W on a omnidirectional antenna. Currently a few coordinated beacons exist in IARU Region 1, in two clusters: | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| border="1" cellspacing="0" cellpadding="5" align="center" | ||
| + | |- style="background: #E7E7FF" | ||
| + | ! Frequency (kHz) | ||
| + | ! TS0 !! TS1 !! TS2 !!TS3 !! TS4 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | align="center" | '''50005''' | ||
| + | | EI0SIX || GB3MCB || PI7SIX || GB3MCB || OZ4BHM | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | align="center" | '''50006''' | ||
| + | | IW9GDC/B || IW9GDC/B || GB3NGI || IW9GDC/B || GB3NGI | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | For more info, refer to: [https://www.rudius.net/oz2m/sbp/ Synchronized Beacon Project] by OZ2M. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==The future of radio propagation beacons== | ||
| + | |||
| + | It seems that there is no longer an interest in HF radio propagation by international organizations, government departments or research institutes, therefore they shall be operated only as part of the [[amateur radio]] service. | ||
| + | |||
| + | A slow process is underway to supplement morse code (CW) identification, which is mostly suitable for aural reception, with digital modulation patterns. The RSGB beacons on 5290 kHz already transmit such code for 30" in each transmission. In the 2011 [[Radio Society of Great Britain|RSGB]] Convention, Bo OZ2M shall talk about the introduction of ''machine generated modulation'' to most radio propagation beacons, in order to enable automatic monitoring. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Beacon timing functions are also modernized. When more beacons share a frequency, they are synchronized by electronic clocks locked to GPS satellite transmissions. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==See also== | ||
| + | * [[Ionosonde]] | ||
| + | * [[Radio beacon]] | ||
| + | * [[JG2XA]]: AN HF Doppler investigation beacon project. | ||
| + | * [[Letter beacon]] | ||
| + | * [[High Frequency Beacon]] | ||
| + | * [[Part_15_Beacons|Part 15 Beacons]] | ||
| + | * [[11_meter#11_meter_Beacon_Frequencies_11m_CB_Beacon_Channels_11m_Beacon_Bands|11 meter band 27 MHz CB radio band beacons]] | ||
| + | * [[HF_pagers|Pagers and data links]] as well [[Remote_Control|High power RC systems]] - de facto 11 meter beacons | ||
==Notes and references== | ==Notes and references== | ||
[[Image:QSL-N7LT-BCN.jpg|thumb|right|QSL card from beacon N7LT/BCN on 28248.5 kHz]] | [[Image:QSL-N7LT-BCN.jpg|thumb|right|QSL card from beacon N7LT/BCN on 28248.5 kHz]] | ||
| - | # Andy Talbot, G4JNT: "Amateur Beacons", ''[[Radio User]]'', ISSN 1748-8117, '''3'''(5), pp.56-58 (May 2008) | + | # Andy Talbot, G4JNT: "Amateur Beacons", ''[[Radio User]]'', ISSN 1748-8117, '''3'''(5), pp.56-58 (May 2008). |
# Andy Talbot, G4JNT: "Amateur Beacons", ''[[Radio User]]'', ISSN 1748-8117, '''3'''(8), pp. 30-33 (August 2008) | # Andy Talbot, G4JNT: "Amateur Beacons", ''[[Radio User]]'', ISSN 1748-8117, '''3'''(8), pp. 30-33 (August 2008) | ||
# [http://www.iaru-r2.org/wp-content/uploads/region-2-mf-hf-bandplan-e.pdf New IARU Region 2 bandplan introduced in January 2008] | # [http://www.iaru-r2.org/wp-content/uploads/region-2-mf-hf-bandplan-e.pdf New IARU Region 2 bandplan introduced in January 2008] | ||
| Line 330: | Line 515: | ||
# [http://www.ham-radio.nl/bakenshf/baken0-20mhz.htm HF 0-20 MHz beacons] | # [http://www.ham-radio.nl/bakenshf/baken0-20mhz.htm HF 0-20 MHz beacons] | ||
# [http://www.itu.int/dms_pub/itu-r/opb/res/R-RES-R.27-1993-PDF-E.pdf ITU Resolution ITU-R 27/1993: HF Field-strength measurement campaign] (PDF) | # [http://www.itu.int/dms_pub/itu-r/opb/res/R-RES-R.27-1993-PDF-E.pdf ITU Resolution ITU-R 27/1993: HF Field-strength measurement campaign] (PDF) | ||
| - | # [http://www.dk0wcy.de/ Aurora beacon DKØWCY] by Deutscher Amateur-Radio-Club e.V.([[DARC]]), 2004. | + | # [http://www.dk0wcy.de/ Aurora beacon DKØWCY] by Deutscher Amateur-Radio-Club e.V. ([[DARC]]), 2004. |
# Pat Hawker, G3VA: "The DK0WCY/DRA5 Propagation Beacons", ''Technical Topics Scrapbook - All 50 years'', [[Radio Society of Great Britain]], ISBN 9781-9050-8639-9, pp. 98 (2008) | # Pat Hawker, G3VA: "The DK0WCY/DRA5 Propagation Beacons", ''Technical Topics Scrapbook - All 50 years'', [[Radio Society of Great Britain]], ISBN 9781-9050-8639-9, pp. 98 (2008) | ||
| - | # Mike Willis, G0MJW: "The GB3RAL VHF Beacon cluster", ''RadCom'', '''84'''(04), [[Radio Society of Great Britain]], pp. 65-59, April 2008 | + | # Mike Willis, G0MJW: "The GB3RAL VHF Beacon cluster", ''RadCom'', '''84'''(04), [[Radio Society of Great Britain]], pp. 65-59, April 2008. |
# The Four meters website: [http://www.70mhz.org/beacons.htm 70 MHz beacon list] | # The Four meters website: [http://www.70mhz.org/beacons.htm 70 MHz beacon list] | ||
# The Four meters website: [http://www.70mhz.org/bandplan_uk.htm RSGB 4m bandplan] | # The Four meters website: [http://www.70mhz.org/bandplan_uk.htm RSGB 4m bandplan] | ||
| Line 338: | Line 523: | ||
# [http://www.radioamateurs-online.fr/2011/03/luxembourg-une-balise-sur-60m-lx0hf/ Luxembourg: Une balise sur 60m LX0HF] Radioamateurs-Online, March 11, 2011. | # [http://www.radioamateurs-online.fr/2011/03/luxembourg-une-balise-sur-60m-lx0hf/ Luxembourg: Une balise sur 60m LX0HF] Radioamateurs-Online, March 11, 2011. | ||
# G. Jacobs, W3ASK, T.J. Cohen, N4XX and R.B. Rose, K6GKU: "The New Shortwave Propagation Handbook", ''CQ Communications, Inc.'', New York, ISBN 0-945016-11-8, pp. 5-17, 5-18. (1995). | # G. Jacobs, W3ASK, T.J. Cohen, N4XX and R.B. Rose, K6GKU: "The New Shortwave Propagation Handbook", ''CQ Communications, Inc.'', New York, ISBN 0-945016-11-8, pp. 5-17, 5-18. (1995). | ||
| + | # Stuart Wisher, G8CYW: "More adventures in optical communications", ''RadCom'', '''88'''(05), [[Radio Society of Great Britain]], pp. 41, May 2012 | ||
| + | # Joe Lynch, N6CL: "VHF Plus", ''CQ Amateur Radio", '''88'''(07), pp. 81, July 2012. | ||
| + | # Rose, R., Hunsucker, R.D. and Lott G.K.: "Results from a year-long Auroral-E measurement campaign", ''Naval Command, Control and Ocean Surveillance Center'', San Diego, CA, April 1993. | ||
| + | # Martin Harrison, G3USF: "Getting started in... beacons, part 1", ''RadCom'', '''89'''(02), [[Radio Society of Great Britain]], pp. 22, February 2013. | ||
| + | # IPS Radio and Space Services: [http://www.ips.gov.au/beacon/vl8ips.html Radio Beacon VL8IPS] (dead link) | ||
| + | # Martin Harrison, G3USF: "Getting started in... beacons, part 2", ''RadCom'', '''89'''(03), [[Radio Society of Great Britain]], pp. 30, March 2013. | ||
| + | # Charlie Newton, G2FKZ: "Radio Auroras", revised edition edited by Steve Telenius-Lowe, 9M6DXX, [[Radio Society of Great Britain]], ISBN 9781-9050-8681-8, pp. 8, 2012. | ||
| + | # [http://www.g4cqm.co.uk/beacons.html 144 MHz Transatlantic Beacon List] by Derek Hilleard G4CQM | ||
| + | # "GB3WGI 144 MHz transatlantic beacon", ''RadCom'', '''89'''(08), [[Radio Society of Great Britain]], pp. 11, August 2013. | ||
| + | # Allocations vary by country. In Australia, VK3RMB is on 10368.536 MHz, VK3RGI on 10368.434 MHz and VK3RXX on 10368.530 MHz. | ||
| + | # According to USA/FCC rules, a Beacon is defined as ''an amateur station transmitting communications for the purposes of observation of propagation and reception or other related experimental activities.'' (Part 79.3.a.9) | ||
| + | # "[https://drive.google.com/file/d/0B5wD1M7AJBTEc0dyUEQtXzVfYjA/view?usp=sharing HF Propagation Beacons]", ''Shortwave Magazine'' , '''59''' (5), ISSN 0037-4261, pp.37, May 2001. | ||
| - | == | + | ==Beacon lists== |
| - | * [ | + | |
| - | * [ | + | Currently there is one regularly updated international beacon list, compiled by Dennis, ZS4BS, and is available on-line. An additional online list by WJ5O contains only 28 MHz (10 meter) beacons. |
| - | * [ | + | |
| + | * Dennis Green, ZS4BS: [https://iaruhfbeacons.wordpress.com/hf-beacons/ Worldwide List of HF Beacons]. | ||
| + | * Martin Harrison, G3USF: [http://www.keele.ac.uk/depts/por/50.htm Worldwide List of 50 Beacons]. | ||
| + | * William H Hays, WJ5O: [http://userpages.troycable.net/~wj5o/bcn.htm Ten meter propagation beacons] | ||
==Further reading== | ==Further reading== | ||
[[Image:IK0WRB-beacon10.png|thumb|right|IK0WRB beacon keyer schematic]] | [[Image:IK0WRB-beacon10.png|thumb|right|IK0WRB beacon keyer schematic]] | ||
* [http://www.ncdxf.org/beacons.html IARU/NDXF International Beacon Project] | * [http://www.ncdxf.org/beacons.html IARU/NDXF International Beacon Project] | ||
| + | * John G. Troster, W6ISQ, & Robert S. Fabry, N6EK: "The NCDXF/IARU International Beacon Network - Part 1", QST, The American Radio Relay League, October 1994, pp. 31-33. | ||
| + | * John G. Troster, W6ISQ, & Robert S. Fabry, N6EK: "The NCDXF/IARU International Beacon Network - Part 2", QST, The American Radio Relay League, November 1994, pp. 49-51. | ||
| + | * John G. Troster, W6ISQ, & Robert S. Fabry, N6EK: "The NCDXF/IARU International Beacon Network - Report and Update", QST, The American Radio Relay League, September 1997, pp. 47-48. | ||
* Ken Reitz, KS4ZR: "[http://www.monitoringtimes.com/MT-10meters.pdf Exploring the World of 10 Meter Beacons]", ''[[Monitoring Times]]'', May 2007, pages 14-16. | * Ken Reitz, KS4ZR: "[http://www.monitoringtimes.com/MT-10meters.pdf Exploring the World of 10 Meter Beacons]", ''[[Monitoring Times]]'', May 2007, pages 14-16. | ||
* R.Wilkinson, G6GVI, S.Cooper, GM4AFF, & B. Hansen, OZ2M: "[http://www.70mhz.org/beacons.htm The 70 MHz Beacon List]", ''The Four Metres Website'', 2008. | * R.Wilkinson, G6GVI, S.Cooper, GM4AFF, & B. Hansen, OZ2M: "[http://www.70mhz.org/beacons.htm The 70 MHz Beacon List]", ''The Four Metres Website'', 2008. | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
* John Jaminet, W3HMS and Charlie Heisler, K3VDB: "Building a beacon for 2401 MHz", ''CQ VHF'', '''10'''(3), CQ Communications, Inc, ISSN 1085-0708, pages 44–46, 2007. | * John Jaminet, W3HMS and Charlie Heisler, K3VDB: "Building a beacon for 2401 MHz", ''CQ VHF'', '''10'''(3), CQ Communications, Inc, ISSN 1085-0708, pages 44–46, 2007. | ||
* Andrew Talbot, G4JNT: [http://www.g4jnt.com/5MHzBcnsWeb.pdf Design and building of the 5 MHz beacons, GB3RAL, GB3WES and GB3ORK]. | * Andrew Talbot, G4JNT: [http://www.g4jnt.com/5MHzBcnsWeb.pdf Design and building of the 5 MHz beacons, GB3RAL, GB3WES and GB3ORK]. | ||
* Andrew Talbot, G4JNT: [http://www.g4jnt.com/BeaconPres-2.ppt The Next Generation of Beacons for the 21st century] (PPT format). | * Andrew Talbot, G4JNT: [http://www.g4jnt.com/BeaconPres-2.ppt The Next Generation of Beacons for the 21st century] (PPT format). | ||
| + | * Alan Gale, G4TMV: "[https://www.ndblist.info/beacons/beacons.pdf An introduction to beacon DXing]", Version 1.0, December 2012. | ||
* UK Microwave Group (UKMuG): [http://www.microwavers.org/indexb.htm UK Amateur Radio & Microwave Beacons]. | * UK Microwave Group (UKMuG): [http://www.microwavers.org/indexb.htm UK Amateur Radio & Microwave Beacons]. | ||
* [http://www.g0afh.com/gb3vhf/index.html GB3VHF – a beacon designed for the 21st Century] | * [http://www.g0afh.com/gb3vhf/index.html GB3VHF – a beacon designed for the 21st Century] | ||
| Line 364: | Line 563: | ||
* [http://users.telenet.be/BEACONCLUSTER/home.html BEACONCLUSTER] worldwide beacon maps by Richard Kaminski ON4CJU. | * [http://users.telenet.be/BEACONCLUSTER/home.html BEACONCLUSTER] worldwide beacon maps by Richard Kaminski ON4CJU. | ||
* [http://brainwagon.org/2009/11/14/another-try-at-an-arduino-based-morse-beacon/ K6HX beacon keyer] using an [http://www.arduino.cc Arduino] microcontroller board. | * [http://brainwagon.org/2009/11/14/another-try-at-an-arduino-based-morse-beacon/ K6HX beacon keyer] using an [http://www.arduino.cc Arduino] microcontroller board. | ||
| + | * [http://www.solorb.com/elect/hamcirc/beacon/index.html WB0RIO Morse Code Beacon Keyer]: a beacon keyer based on CMOS digital componets, by G. Forrest-Cook, WB0RIO (1996). | ||
| + | * [http://www.ac6v.com/beacons.htm Beacons a Bunch]: software resources for monitoring IARU/NCDXF beacons, compliled by Jeff Dinkins, AC6V. | ||
| + | * [http://www.earf.co.uk/light_beacon.htm Low power 628nm (red) light beacon], co-sited with GB3CAM beacons at Wyton | ||
| + | * [http://www.on0eme.org ON0EME moon beacon status] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | {| border="1" cellspacing="0" cellpadding="5" align="center" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | '''FCC rules, §97.203 Beacon station.''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | * (a) Any amateur station licensed to a holder of a Technician, Technician Plus, General, Advanced or Amateur Extra Class operator license may be a beacon. A holder of a Technician, Technician Plus, General, Advanced or Amateur Extra Class operator license may be the control operator of a beacon, subject to the privileges of the class of operator license held. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * (b) A beacon must not concurrently transmit on more than 1 channel in the same amateur service frequency band, from the same station location. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * (c) The transmitter power of a beacon must not exceed 100 W. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * (d) A beacon may be automatically controlled while it is transmitting on the 28.20-28.30 MHz, 50.06-50.08 MHz, 144.275-144.300 MHz, 222.05-222.06 MHz, or 432.300-432.400 MHz segments, or on the 33 cm and shorter wavelength bands. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * (e) Before establishing an automatically controlled beacon in the National Radio Quiet Zone or before changing the transmitting frequency, transmitter power, antenna height or directivity, the station licensee must give written notification thereof to the Interference Office, National Radio Astronomy Observatory, P.O. Box 2, Green Bank, WV 24944. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ** (1) The notification must include the geographical coordinates of the antenna, antenna ground elevation above mean sea level (AMSL), antenna center of radiation above ground level (AGL), antenna directivity, proposed frequency, type of emission, and transmitter power. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ** (2) If an objection to the proposed operation is received by the FCC from the National Radio Astronomy Observatory at Green Bank, Pocahontas County, WV, for itself or on behalf of the Naval Research Laboratory at Sugar Grove, Pendleton County, WV, within 20 days from the date of notification, the FCC will consider all aspects of the problem and take whatever action is deemed appropriate. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * (f)A beacon must cease transmissions upon notification by a District Director that the station is operating improperly or causing undue interference to other operations. The beacon may not resume transmitting without prior approval of the District Director. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * (g) A beacon may transmit one-way communications. | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==External links== | ||
| + | # [http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aF8zc8zRaok 10 Meter Amateur Radio Propagation CW Beacon Demo] by KI7F (Youtube video). | ||
| + | # [http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8dyDte9kSkU 10 Meter beacon equipment]: Modified CB radio using a freakin` beacon controller (Youtube video). | ||
| + | # [http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Uy3ufVTsqKE Arduino Morse Beacon Keyer] by Mark VandeWettering K6HX (Youtube video). | ||
| - | {{CC-BY-SA-WP| | + | {{CC-BY-SA-WP|Amateur_radio_propagation_beacon}} |
[[Category:Beacons]] | [[Category:Beacons]] | ||
Latest revision as of 14:09, 24 March 2023
A radio propagation beacon is a radio beacon, which is mainly used for investigating the propagation of radio signals. Currently most radio propagation beacons use amateur radio frequencies.(26) They can be found on HF, VHF, UHF, and microwave frequencies. Microwave beacons are also used as signal sources to test and calibrate antennas and receivers.[1] [2] Andy Talbot, G4JNT, gives the following definition for beacons licensed in the Amateur Radio service: A station in the Amateur Service or Amateur Satellite Service that autonomously transmits in a fixed format, which may include repeated data or information, for the study of propagation, determination of frequency or bearing, or for other experimental purposes.[1]
History
The earliest record of radio propagation beacons goes back to World War II, when the German military operated propagation beacons on wavelengths of approximate 80 m and 10 m. Many propagation beacons were installed during the International Geophysical Year 1957-1958 These included amateur radio beacons OZ7IGY and GB3IGY (later GB3RAL) on 144 MHz, which are still operational, as well as the now defunct DM3IGY in East Germany on 28001 kHz. (19) GB3IGY transmitted with the unusual for the time high power of 1 kW. It was situated at Badgers Mount, Sevenoaks, England and was operated by Ken Ellis, G5KW.(22)
Transmission characteristics
The majority of propagation beacons operate in continuous wave (CW or A1A) and transmit their identification (callsign and location) in Morse code. Some of them send long dashes (sometimes at varying power levels) to facilitate signal strength measurement. A small number of beacons transmit Morse code by frequency shift keying (F1A). A few beacons transmit signals in digital modulation modes, like radioteletype (F1B) and PSK31 (G1B).
Most beacons consist of a simple digital keyer, based on discrete digital electronics or a microcontroller, and a low power transmitter or tranceiver. FT-897, a budget HF tranceiver produced by Yaesu/Vertex, has a programmable beacon mode and is used in some temporary propagation beacon installations. Recently K6HX published a versatile Morse code keyer design based on the popular Arduino microcontroller platform.
Antennas usually are types with low directivity. There are exceptions, however, like the high power beacons with directional antennas, specifially set up for transatlantic VHF propagation experiments.
160 meters beacons
The IARU Region 2 (North and South America) bandplan reserves the range 1999 kHz to 2000 kHz for propagation beacons.
60 meters beacons
In addition to the DARC and RSBG beacon projects on 5195 and 5290 kHz (see below), Eddie Bellerby of UDXF discovered in March 2011 a new CW beacon on 5206 kHz, sending LX0HF, presumably from Luxembourg.[13] Further intelligence indicates that the beacon is operated by Philippe LX2A/LX7I of the Luxembourg Amateur Radio Society.[14] Two more european beacons are listed on 5 MHz, OV1BCN on 5290 kHz, operated by OZ1FJB and OK1IF on 5258.5 kHz from the Czech Republic, though their current status is unclear.
| Callsign | Frequency | Locator | Details |
|---|---|---|---|
| DRA5 | 5195.0 kHz | JO44VQ | DARC |
| LX0HF | 5205.2 kHz | JN39dr | Radioamateurs du Luxembourg [1] |
| HG7BHB | 5252.3 kHz | JN97LE | |
| OK1IF | 5258.5 kHz | JO40HG | Inactive. Recording: [2] |
| GB3RAL | 5290.0 kHz | IO91IN | RSGB, inactive |
| GB3WES | 5290.0 kHz | IO84QN | RSGB, inactive |
| GB3ORK | 5290.0 kHz | IO89JA | RSGB, inactive |
| OV1BCN | 5290.5 kHz | JO55SI | Op OZ1FJB [3] |
| HB9AW | 5291.0 kHz | JN47BE | [4] |
| SZ1SV | 5398.5 kHz | KM17UX | Op SV1IW & SV1JG. Inactive. |
30 meters beacons
| Callsign | Frequency | Locator | Details |
|---|---|---|---|
| DK0WCY | 10144.0 kHz | JO44VQ | DARC |
| IK3NWX | 10137.3 kHz | JN55VF | nr Monselice, PD 15m asl |
10 meters beacons
Most HF radio propagation beacons are found in the 10 meters (28 MHz) frequency band, where they are good indicators of Sporadic E ionospheric propagation. According to IARU bandplans, the following 28 MHz frequencies are allocated to radio propagation beacons:
| IARU Region | Beacon allocations |
|---|---|
| R1 |
|
| R2[3] |
|
| R3 |
|
40 MHz beacons
- The first radio propagation beacon on 40 MHz is OZ7IGY in Jystrup, Denmark (JO55WM) and transmits on 40071 kHz
40021 kHz(40.071 MHz). Transmitted power is 20 W to a dipole antenna. The beacon is frequency- and time-locked to GPS. The sequence is programmed to send PI4 , followed by a short pause, and then the call sign and grid locator sent in CW, then a pause, and a carrier until start of the next cycle. PI4 is a digital mode specifically designed for beacons and propagation studies, similar to JT4 and WSPR. To decode PI4, tune 800 Hz below the nominal frequency. - The Radio Society of Great Britain has a license for beacon transmissions from GB3RAL (Didcot, UK) on 40050 & 60050 kHz (40.050 MHz & 60.050 MHz - 8 meters and 5 meters).
- While not a beacon by design, the US Government's SNOTEL telemetry system on 40 MHz operates more than 600 transmitters (mostly in the Rocky Mountain and Western United States regions) on 40670 kHz (40.670 MHz, 40.67 MHz). During sporadic-E band openings, data bursts from the SNOTEL system can be heard on 40.67 MHz.
- The Canadian military base Shuffield (CYSD) in Alberta operates a FM mode military VHF FM radio beacon transmitting continuously with a CW ID / a Morse code ID YSD followed by a tone burst on 36.6 FM (36600 kHz FM, 36.600 MHz FM, 36.60 FM, 36.6 MHz).
6 meters (50 MHz) beacons
In the 6 meters (50 MHz) band, beacons traditionally operate in the lower part of the band, in the range 50000 kHz to 50080 kHz. Due to unpredictable and intermittent long distance propagation, usually achieved by a combination of ionospheric conditions, beacons are very important in providing early warning for 50 MHz openings.
The ARRL bandplan recommends 50060 to 50080 kHz for beacons in the United States.
In Australia beacons operate from 50280 to 50350 kHz.
The new IARU Region 1 bandplan moves 50 MHz beacons, with the exception of beacons participating to the Synchronized Beacon Project, in a new allocation, 50400 to 50500 kHz.
4 meters (70 MHz) beacons
General beacon operations
Numerous beacons operate on 70 MHz in recent years. Their main purrpose is to dected the relativley rare and extreme Es (sporadic E) opennings, which exceed 70 MHz.
There is no definite international beacon allocation, due to various countries having different amateur radio allocations in this band. Generally beacons operate near the bottom end (70.000-70.100 MHz).(11) (12). Most respect the RSGB bandplan, staying below 70.050 MHz.
- 70.000-70.050 MHz: UK beacon allocation, including personal beacons on 70.030 MHz
Special beacon allocations
- USA: 70.005 MHz is allocated to the WE9XFT beacon. Transmits from Bedford, VA, under an FCC experimental license issued to Brian Justin, WA1ZMS, with a power of 3 kW. In 2012 this beacon shall transmit from the same location under new callsign WF9XRU.
- Austria: 70.045 MHz is allocated to the OE5QL beacon.
- Hong Kong: 71.757 MHz is allocated to the VR2FOUR beacon.
VHF/UHF beacons
Beacons on 144 MHz and higher frequencies are mainly used to identify tropospheric radio propagation openings. It is not uncommon for VHF and UHF beacons to use directional antennas. Frequency allocations for beacons on VHF and UHF bands vary widely in different ITU/IARU regions and countries.
| Band | Beacon Sub-band (MHz) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| IARU R1 | IARU R2 | IARU R3 | |
| 2 m | 144.400-144.490 | 144.275–144.300 | Unknown |
| 1.25 m | N/A | 222.050–222.060 | N/A |
| 70 cm | 432.800-432.990 | 432.300–432.400 | Unknown |
| 33 cm | N/A | Varies Locally | N/A |
| 23 cm | 1,296.800-1,296.990 | 1,296.070-1,296.080 | Unknown |
| 13 cm | 2,320.800-2,320.990 | 2,304.300-2,304.400 | Unknown |
The current allocation in the United Kingdom, which also reflects IARU Region 1 recommendations, is the following:[4]
| Band | Beacon allocation (kHz) |
|---|---|
| 4 m | 70,000-70,030 |
| 2 m | 144,400-144,490 |
| 70 cm | 432,800-432,990 |
| 23 cm | 1296,800-1296,990 |
ON0EME moon beacon
A beacon specifically for earth-moon-earth (EME or "moonbounce") reception became operational in 2012 in Belgium. The beacon uses call sign ON0EME and transmits on 1296.0 MHz with a very high power of 1000 kW ERP. The antenna is a solid parabolic reflector with a diameter of 3.7 m. [17]
144 MHz transatlantic beacons
A number of VHF beacons have been installed on both shores of the Atlantic Ocean, as an early warning system for exceptional sporadic-E (Es) conditions, which shall allow transatlantic QSOs on 2 m. The followng list includes most beacons, not all of them are always operational.[23]
| Callsign | Locator | Frequency (kHz) | Info |
|---|---|---|---|
| CU2VHF | HM77DT | 144401 | |
| CU8DUB | HM49KL | 144420 | |
| D4C/B | HK76MV | 144436 | 750 m ASL, 20W CW. Copied by Dave Pedersen, PJ4VHF/N7BHC, on Bonaire Island on May 6, 2015 [5] |
| ED8ZAA/B | IL18 | 144484 | |
| GB3WGI[24] | IO64BL | 144487 | 100 W CW and JT65. Activated on June 4, 2013. |
| K4MHZ | FM25 | 144300 | 2M Transatlantic Beacon, Hatteras, NC: CW at 10 WPM. Running 100W to a 12 element long Yagi at 50' on a center azimuth of 70 degrees towards the Azores, Canary Islands, and southern Europe/North Africa. |
| N7BHC | FM15PA | 144291 | Mode: CW, 13 WPM. Transmit sequence: N7BHC FM15PA N7BHC FM15PA N7BHC FM15PA (15 second carrier) (15 seconds receive period). Location: 35.0302 N - 76.7146 W |
| NP2X/B | FK77PR | 144291 | St. Croix, US Virgin Islands - 240 feet AMSL (73 meters AMSL) - RF Concepts 160 watt, reduced to 100 watts for beacon operation - 15 element yagi @ beam heading of 55 degrees (Portgual) - np2xbeacon@gmail.com |
| PY2MTV/B | GG66va | 144300 | Beaming to AF/EU |
| VE1SMU/H | 144.288 | ||
| VO1ZA | GN37JS | 144400 | Inactive |
| W1RJA/B | FN41CJ | 144282 | Southern Rhode Island. Emission: A1 (amplitude keyed CW) Power: 60 Watts Feedline: 160' Cablewave FLC 12-50 half inch hardline. Antenna: 9.5 dBd 5 element yagi beaming 60 degrees azimuth. Height: 140 feet (43M) above base elevation of 130 feet (40M) ASL |
| WA1ZMS | FM07FM | 144285 | Activated on October 29, 2006 - 4200FT AMSL - Antenna: 2-yagi pair, Directive Systems DPM144-5 Antenna gain: 11.5dBd Radiated power: 1400W ERPd) |
Indian Ocean beacon project
An Australian ham radio group has set up a beacon to investigate if there is any VHF ducting between Australia and South Africa. Beacon VK6RIO is located in Perth, W. Australia and operates on 144.950 MHz. The beacon transmits 100 watts into four 8-element Yagis with digital Chirp modulation. This special modulation scheme can be detected some 50 dB below the noise floor.
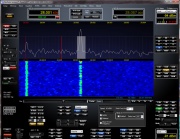
The beacon is GPS locked both in frequency, time and Chirp synchronisation. In order to detect the Chirp beacon, the receiving station requires a GPS locked Software Defined Radio (SDR), a GPS locked 144 MHz down-converter and 1 PPS signal from a GPS receiver to time stamp received signals. Open source PC software by Hermann, DL3HVH, shall be made available for processing the received signals.
SHF and microwave beacons
In addition to identifying propagation, microwave beacons are also used as signal sources to test and calibrate antennas and receivers. SHF beacons are not as common as beacons on the lower bands, and beacons above the 3 cm (10 GHz) band are unusual.
| Band | Beacon Sub-band (MHz) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| IARU R1 | IARU R2 | IARU R3 | |
| 9 cm | 3,400.800-3,400.995 | 3,456.300-3,456.400 | Unknown |
| 5 cm | 5,760.800-5,760.995 | 5,760.300-5,760.400 | Unknown |
| 3 cm | 10,368.800-10,368.995 | 10,368.300-10,368.400 | Unknown (25) |
| 1.2 cm | 24,048.800-24,048.995 | Beacons are rare | |
Optical and infrared beacons
Recently some groups of radio amateurs, especially in Great Britain, experiment with two-way communications on optical wavelengths. This activity has led to the design and installation of a few beacons operating on optical wavelengths. These beacons transmit modulated light using high intensity LEDs and are used mainly for equipment setting and calibration. An interesting example is the optical beacon located at GB3CAM (Wyton, UK) operating at 628 nm.[16]
License-free experimental beacons
These are extremely low power experimental beacons which operate legally without a license on specific bands, which are reserved for very short range radio transmissions or for industrial, scientific and medical devices (ISM) and in which a limited level of radiated RF energy is allowed. They are operated as radio propagation experiments by radio amateurs and other radio hobbyists.
| Type | Frequencies | Countries | FCC Part 15 rules |
|---|---|---|---|
| LowFER | 160-190 kHz | USA, Canada | § 15.217 |
| MedFER | 510 & 1704 kHz (510-1705 kHz) | USA, Canada | § 15.219 |
| BeFER | 6776 kHz | Canada | - |
| HiFER | 13553-13567 kHz | USA, Canada | § 15.225 |
| 49ers | 49846 kHz (49820-49900 kHz) | USA | § 15.235 |
Beacon projects
Most radio propagation beacons are operated by individual radio amateurs or amateur radio societies and clubs. As a result, there are frequent additions and deletions to the lists of beacons. There are, however a few major projects coordinated by organizations like the International Telecommunications Union and the International Amateur Radio Union.
IARU/NCDXF HF Beacon Project
The International Beacon Project (IBP), which is coordinated by the Northern California DX Foundation (NCDXF) and the International Amateur Radio Union (IARU), consists of 18 HF propagation beacons worldwide, which transmit in turns on 14100 kHz, 18110 kHz, 21150 kHz, 24930 kHz, and 28200 kHz. [5] The IARU/NDXF beacons transmit in turns on the five designated frequencies according to the following schedule, which repeats every 3 minutes:
| Slot | DXCC entity | Call | Location | Latitude | Longitude | Grid Sq | 14100 | 18110 | 21150 | 24930 | 28200 | Operator |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 01 | United Nations | 4U1UN | New York City | 40º 45' N | 73º 58' W | FN3ØAS | 00.00 | 00.10 | 00.20 | 00.30 | 00.40 | UNRC |
| 02 | Canada | VE8AT | Eureka, Nunavut | 79º 59' N | 85º 57' W | EQ79AX | 00.10 | 00.20 | 00.30 | 00.40 | 00.50 | RAC |
| 03 | United States | W6WX | Mt. Umunhum | 37º 09' N | 121º 54' W | CM97BD | 00:20 | 00.30 | 00:40 | 00.50 | 01:00 | NCDXF |
| 04 | Hawaii | KH6WO | Laie | 21º 38' N | 157º 55' W | BL11AP | 00.30 | 00.40 | 00.50 | 01.00 | 01.10 | (Off) |
| 05 | New Zealand | ZL6B | Masterton | 41º 03' S | 175º 36' E | RE78TW | 00.40 | 00.50 | 01.00 | 01.10 | 01.20 | NZART |
| 06 | Australia | VK6RBP | Rolystone | 32º 06' S | 116º 03' E | OF87AV | 00.50 | 01.00 | 01.10 | 01.20 | 01.30 | WIA |
| 07 | Japan | JA2IGY | Mt. Asama | 34º 27' N | 136º 47' E | PM84JK | 01.00 | 01.10 | 01.20 | 01.30 | 01.40 | JARL |
| 08 | Russia | RR9O | Novosibirsk | 54º 59' N | 82º 54' E | NO14KX | 01.10 | 01.20 | 01.30 | 01.40 | 01.50 | SRR |
| 09 | Hong Kong | VR2B | Hong Kong | 22º 16' N | 114º 09' E | OL72BG | 01.20 | 01.30 | 01.40 | 01.50 | 02.00 | HARTS |
| 10 | Sri Lanka | 4S7B | Colombo | 6º 6' N | 80º 13' E | NJ06CC | 01.30 | 01.40 | 01.50 | 02.00 | 02.10 | RSSL |
| 11 | South Africa | ZS6DN | Pretoria | 25º 54' S | 28º 16' E | KG44DC | 01:40 | 01.50 | 02:00 | 02:10 | 02:20 | ZS6DN |
| 12 | Kenya | 5Z4B | Kariobangi | 1º 15' S | 36º 53' E | KI88KS | 01.50 | 02.00 | 02.10 | 02.20 | 02.30 | ARSC |
| 13 | Israel | 4X6TU | Tel Aviv | 32º 03' N | 34º 46' E | KM72JB | 02:00 | 02:10 | 02:20 | 02.30 | 02:40 | IARC |
| 14 | Finland | OH2B | Lohja | 60º 19' N | 24º 50' E | KP2Ø | 02:10 | 02:20 | 02:30 | 02:40 | 02:50 | SRAL |
| 15 | Madeira | CS3B | Santo da Serra | 32º 43' N | 16º 48' W | IM12OR | 02.20 | 02.30 | 02.40 | 02.50 | 00.00 | ARRM |
| 16 | Argentina | LU4AA | Buenos Aires | 34º 37' S | 58º 21' W | GFØ5TJ | 02:30 | 02:40 | 02:50 | 00.00 | 00:10 | ARC |
| 17 | Peru | OA4B | Lima | 12º 04' S | 76º 57' W | FH17MW | 02.40 | 02.50 | 00.00 | 00.10 | 00.20 | RCP |
| 18 | Venezuela | YV5B | Caracas | 10º 25' N | 66º 51' W | FK6ØNJ | 02:50 | 00.00 | 00:10 | 00:20 | 00:30 | RCV |
The original NCDXF/IARU beacon project, coordinated by John W6ISQ, consisted of nine 100W beacons which operated only on 14100 kHz on a coordinated 10 minute sequence. The beacons used to send a longer callup sequence, like "QST DE 4U1UN/B BEACON" followed by dashes with 100 W, 10 W, 1 W, and 100 mW, finally ending with "4U1UN/B SK". The original beacons were 4U1UN/B, W6WX/B, KH6O/B, JA2IGY, 4X6TU, OH2B, CT3B, ZS6DN and LU4AA. This network evolved into its current format with 18 beacons on five frequencies around 1999.(15) The current beacons consist of a Kenwood TS-50 tranceiver, a beacon controller, a vertical antenna and a GPS unit.
ITU sponsored beacons
As part of an International Telecommunications Union-funded project, radio propagation beacons were installed by national authorities at Sveio, Norway (callsign LN2A, 59.60420N - 5.291670E) and at Darwin, Australia (callsign VL8IPS, 12.60420S - 131.29200E). The beacons operated on frequencies 5471.5 kHz, 7871.5 kHz, 10408.5 kHz, 14396.5 kHz, and 20948.5 kHz.(6) (15) (27) Since 2002, there have been no reception reports for these beacons and the relevant ITU web pages have been removed. (7) (20)
| HF Field-Strength measurement campaign
For a number of years, ITU-R Study Group 3 has been promoting a world-wide HF field-strength measurement campaign, the impetus for which arose from WARC HFBC-87 and the request for improved accuracy in HF propagation prediction. At that time, the Study Group recognised that significant improvements in HF propagation prediction methods needed a substantial body of new measurement data and to that end, administrations and organisations were invited to participate in the measurement campaign, either by installing suitable transmitters or by collecting long-term data from appropriate receiving systems. The campaign is specified in Recommendation ITU-R P.845 'HF field-strength measurement' and comprises a world-wide network of transmitters and receivers using coded transmissions on pre-determined frequencies. The reasons for the campaign and the continuing need for participation in it, are underlined in Resolution ITU-R 27 (HF field-strength measurement campaign). So far, regular transmissions are being provided by the Administrations of Australia and Norway. Details of the transmitter in Norway, operated by the Norwegian Telecommunications Authority and Telenor Broadcasting, are given below: | ||||||||||||
Radio Beacon LN2A
Administrations and organizations participating in the work of ITU-R are invited to consider the possibility of participating in the campaign, either through the provision of transmissions or by the collection of field strength measurement data, both in accordance with the specifications given in Recommendation ITU-R P.845. For further details on the campaign, including the availability of a suitable receiving system, please contact the ITU-R Counsellor for Study Group 3 (Dr. Kevin A. Hughes) at ITU Headquarters, in Geneva. The Norwegian Telecommunications Authority and Telenor Broadcasting would be pleased to acknowledge reception reports of LN2A with a QSL card. The contact address is: Norwegian Telecommunications Authority (Att. AYO/TF) | ||||||||||||
| Radio Beacon VL8IPS
This beacon was established by IPS Radio and Space Services in conjuction with thw Royal Australian Navy.
|
DARC beacon project
The Deutscher Amateur Radio Club (DARC) sponsors two beacons which transmit from Scheggerott, near Kiel (54.68750N - 9.791670E, JO44VQ). [8] These beacons are DRA5 on 5195 kHz and DK0WCY on 10144 kHz. In addition to identification and location, every 10 minutes these beacons transmit solar, geomagnetic and ionospheric bulletins. Transmissions are in Morse code (CW) for aural reception, RTTY (45 baud 170 Hz at HH+10) and PSK31 (at HH+50). [9] DK0WCY operates also a limited service beacon on 3579 kHz at 0720-0900 and 1600-1900 local time.
RSGB 5 MHz beacon project
The Radio Society of Great Britain (RSGB) operates three radio propagation beacons on 5290 kHz, which transmit in sequence, for one minute each, every 15 minutes. The project includes GB3RAL near Didcot (51.56250N - 1.291670W, IO91IN), GB3WES in Cumbria (54.56250N - 2.6250W, IO84QN) and GB3ORK in the Orkney Islands (59.02080N - 3.208330W, IO89JA).
Beacon GB3RAL, which is located at the Rutherford-Appleton Laboratory (RAL), also transmits continuously on 28215 kHz and on a number of low VHF frequencies (40050, 50053, 60053 and 70053 kHz).[10]
As of August 2017 the 5 MHz beacon at Didcot is not operational. The other two beacons are active. In addition to Morse code, beacon GB3ORK also transmits in JT9 on the minute following its regular transmission.
A radio propagation beacon with callsign NAF was installed in 1983 at Cape Prince, Wales, AK. It transmitted both CW and FSK identification with 100 W to a three-band fan dipole on 5604, 11004 and 16804 kHz. The project, which included reception sites at Fairbanks, AK, Seattle, WA, State College, PA and San Diego, CA, was coordinated by the U.S. Naval Security Group Command and its purpose was to verify and calibrate HF propagation prediction software. (15) It is not known when the project was terminated.
Another propagation beacon was installed in 1991 at the Arctic Submarine Laboratory at Cape Prince of Wales, AK. The beacon operated on 25545 kHz (25.545 MHz) and tranmitted the morse code letter "R". A reception facility existed at Fairbanks, AK, some 900 km away. The R beacon was used to study aurora and sporadic E events at high geographical latitudes.(18)
WSPR Network
This is an a large scale amateur radio propagation beacon project which uses the WSPR (Weak Signal Propagation Reporter) transmission scheme available with the WSJT software suite, created by Joe Taylor, K1JT. The loosely-coordinated beacon transmitters and receivers, collectively known as the WSPRnet, report the real-time propagation characteristics of a number of frequency bands and geographical locations via the Internet. The WSPRnet website provides detailed propagation report databases and real-time graphical maps of propagation paths. WSPR Network operates on the following amateur radio frequencies (USB dial settings in kHz) 136.0, 502.4, 1836.6, 3592.6, 5287.2, 7038.6, 101387.0, 14095.6, 18104.6, 21094.6, 24924.6, 28124.6, 50293.0, 70028.6 and 144489.0 kHz.
IARU 50 MHz Synchronized Beacon Project (SBP)
IARU promotes a network of synchronized beacons worldwide at the lower part of the 50 MHz (6m) band. Each IARU region is allocated a 10 kHz segment, which is divided into ten 1 kHz wide beacon channels.
| IARU Region | Beacon frequencies (kHz) |
|---|---|
| R1 | 50000, 50001, 50002, 50003, 50004, 50005, 50006, 50007, 50008, 50009 |
| R2 | 50010, 50011, 50012, 50013, 50014, 50015, 50016, 50017, 50018, 50019 |
| R3 | 50020, 50021, 50022, 50023, 50024, 50025, 50026, 50027, 50028, 50029 |
Each frequency can accomodate up to five beacons, which transmit sequentially in time slots (TS) 0 to 4. The transmission mode and sequence for each beacon is "PI4 - CW ID - carrier", lasting exactly one minute. SBP beacons transmit with 25W on a omnidirectional antenna. Currently a few coordinated beacons exist in IARU Region 1, in two clusters:
| Frequency (kHz) | TS0 | TS1 | TS2 | TS3 | TS4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50005 | EI0SIX | GB3MCB | PI7SIX | GB3MCB | OZ4BHM |
| 50006 | IW9GDC/B | IW9GDC/B | GB3NGI | IW9GDC/B | GB3NGI |
For more info, refer to: Synchronized Beacon Project by OZ2M.
The future of radio propagation beacons
It seems that there is no longer an interest in HF radio propagation by international organizations, government departments or research institutes, therefore they shall be operated only as part of the amateur radio service.
A slow process is underway to supplement morse code (CW) identification, which is mostly suitable for aural reception, with digital modulation patterns. The RSGB beacons on 5290 kHz already transmit such code for 30" in each transmission. In the 2011 RSGB Convention, Bo OZ2M shall talk about the introduction of machine generated modulation to most radio propagation beacons, in order to enable automatic monitoring.
Beacon timing functions are also modernized. When more beacons share a frequency, they are synchronized by electronic clocks locked to GPS satellite transmissions.
See also
- Ionosonde
- Radio beacon
- JG2XA: AN HF Doppler investigation beacon project.
- Letter beacon
- High Frequency Beacon
- Part 15 Beacons
- 11 meter band 27 MHz CB radio band beacons
- Pagers and data links as well High power RC systems - de facto 11 meter beacons
Notes and references
- Andy Talbot, G4JNT: "Amateur Beacons", Radio User, ISSN 1748-8117, 3(5), pp.56-58 (May 2008).
- Andy Talbot, G4JNT: "Amateur Beacons", Radio User, ISSN 1748-8117, 3(8), pp. 30-33 (August 2008)
- New IARU Region 2 bandplan introduced in January 2008
- Amateur Radio UK VHF Bandplan, Great Yarmouth Radio Club
- International Beacon Project by the Northern California DX Foundation (2008)
- HF 0-20 MHz beacons
- ITU Resolution ITU-R 27/1993: HF Field-strength measurement campaign (PDF)
- Aurora beacon DKØWCY by Deutscher Amateur-Radio-Club e.V. (DARC), 2004.
- Pat Hawker, G3VA: "The DK0WCY/DRA5 Propagation Beacons", Technical Topics Scrapbook - All 50 years, Radio Society of Great Britain, ISBN 9781-9050-8639-9, pp. 98 (2008)
- Mike Willis, G0MJW: "The GB3RAL VHF Beacon cluster", RadCom, 84(04), Radio Society of Great Britain, pp. 65-59, April 2008.
- The Four meters website: 70 MHz beacon list
- The Four meters website: RSGB 4m bandplan
- Southgate Amateur Radio Club: Luxembourg 60m beacon LX0HF
- Luxembourg: Une balise sur 60m LX0HF Radioamateurs-Online, March 11, 2011.
- G. Jacobs, W3ASK, T.J. Cohen, N4XX and R.B. Rose, K6GKU: "The New Shortwave Propagation Handbook", CQ Communications, Inc., New York, ISBN 0-945016-11-8, pp. 5-17, 5-18. (1995).
- Stuart Wisher, G8CYW: "More adventures in optical communications", RadCom, 88(05), Radio Society of Great Britain, pp. 41, May 2012
- Joe Lynch, N6CL: "VHF Plus", CQ Amateur Radio", 88(07), pp. 81, July 2012.
- Rose, R., Hunsucker, R.D. and Lott G.K.: "Results from a year-long Auroral-E measurement campaign", Naval Command, Control and Ocean Surveillance Center, San Diego, CA, April 1993.
- Martin Harrison, G3USF: "Getting started in... beacons, part 1", RadCom, 89(02), Radio Society of Great Britain, pp. 22, February 2013.
- IPS Radio and Space Services: Radio Beacon VL8IPS (dead link)
- Martin Harrison, G3USF: "Getting started in... beacons, part 2", RadCom, 89(03), Radio Society of Great Britain, pp. 30, March 2013.
- Charlie Newton, G2FKZ: "Radio Auroras", revised edition edited by Steve Telenius-Lowe, 9M6DXX, Radio Society of Great Britain, ISBN 9781-9050-8681-8, pp. 8, 2012.
- 144 MHz Transatlantic Beacon List by Derek Hilleard G4CQM
- "GB3WGI 144 MHz transatlantic beacon", RadCom, 89(08), Radio Society of Great Britain, pp. 11, August 2013.
- Allocations vary by country. In Australia, VK3RMB is on 10368.536 MHz, VK3RGI on 10368.434 MHz and VK3RXX on 10368.530 MHz.
- According to USA/FCC rules, a Beacon is defined as an amateur station transmitting communications for the purposes of observation of propagation and reception or other related experimental activities. (Part 79.3.a.9)
- "HF Propagation Beacons", Shortwave Magazine , 59 (5), ISSN 0037-4261, pp.37, May 2001.
Beacon lists
Currently there is one regularly updated international beacon list, compiled by Dennis, ZS4BS, and is available on-line. An additional online list by WJ5O contains only 28 MHz (10 meter) beacons.
- Dennis Green, ZS4BS: Worldwide List of HF Beacons.
- Martin Harrison, G3USF: Worldwide List of 50 Beacons.
- William H Hays, WJ5O: Ten meter propagation beacons
Further reading
- IARU/NDXF International Beacon Project
- John G. Troster, W6ISQ, & Robert S. Fabry, N6EK: "The NCDXF/IARU International Beacon Network - Part 1", QST, The American Radio Relay League, October 1994, pp. 31-33.
- John G. Troster, W6ISQ, & Robert S. Fabry, N6EK: "The NCDXF/IARU International Beacon Network - Part 2", QST, The American Radio Relay League, November 1994, pp. 49-51.
- John G. Troster, W6ISQ, & Robert S. Fabry, N6EK: "The NCDXF/IARU International Beacon Network - Report and Update", QST, The American Radio Relay League, September 1997, pp. 47-48.
- Ken Reitz, KS4ZR: "Exploring the World of 10 Meter Beacons", Monitoring Times, May 2007, pages 14-16.
- R.Wilkinson, G6GVI, S.Cooper, GM4AFF, & B. Hansen, OZ2M: "The 70 MHz Beacon List", The Four Metres Website, 2008.
- John Jaminet, W3HMS and Charlie Heisler, K3VDB: "Building a beacon for 2401 MHz", CQ VHF, 10(3), CQ Communications, Inc, ISSN 1085-0708, pages 44–46, 2007.
- Andrew Talbot, G4JNT: Design and building of the 5 MHz beacons, GB3RAL, GB3WES and GB3ORK.
- Andrew Talbot, G4JNT: The Next Generation of Beacons for the 21st century (PPT format).
- Alan Gale, G4TMV: "An introduction to beacon DXing", Version 1.0, December 2012.
- UK Microwave Group (UKMuG): UK Amateur Radio & Microwave Beacons.
- GB3VHF – a beacon designed for the 21st Century
- IK0WRB beacon keyer, based on a PIC16F84 microcontroller.
- Aurora Beacon DK0WCY
- OV1BCN: a new HF propagation beacon on 5290.5 kHz.
- BEACONCLUSTER worldwide beacon maps by Richard Kaminski ON4CJU.
- K6HX beacon keyer using an Arduino microcontroller board.
- WB0RIO Morse Code Beacon Keyer: a beacon keyer based on CMOS digital componets, by G. Forrest-Cook, WB0RIO (1996).
- Beacons a Bunch: software resources for monitoring IARU/NCDXF beacons, compliled by Jeff Dinkins, AC6V.
- Low power 628nm (red) light beacon, co-sited with GB3CAM beacons at Wyton
- ON0EME moon beacon status
FCC rules, §97.203 Beacon station.
|
External links
- 10 Meter Amateur Radio Propagation CW Beacon Demo by KI7F (Youtube video).
- 10 Meter beacon equipment: Modified CB radio using a freakin` beacon controller (Youtube video).
- Arduino Morse Beacon Keyer by Mark VandeWettering K6HX (Youtube video).
| | This article contains textual material from Wikipedia (TM). Wikipedia texts are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike license. In short: you are free to distribute and modify the text as long as you attribute its author(s) or licensor(s). If you alter, transform, or build upon this work, you may distribute the resulting work only under the same or similar license to this one. Wikipedia article: Amateur_radio_propagation_beacon | WP |
This site is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon.com. Some links may be affiliate links. We may get paid if you buy something or take an action after clicking one of these.